This best practice describes an open schooling initiative developed by UFSC university and 12 secondary schools in Santa Catarina – Brazil.
It was supported by the Open University OU-UK.
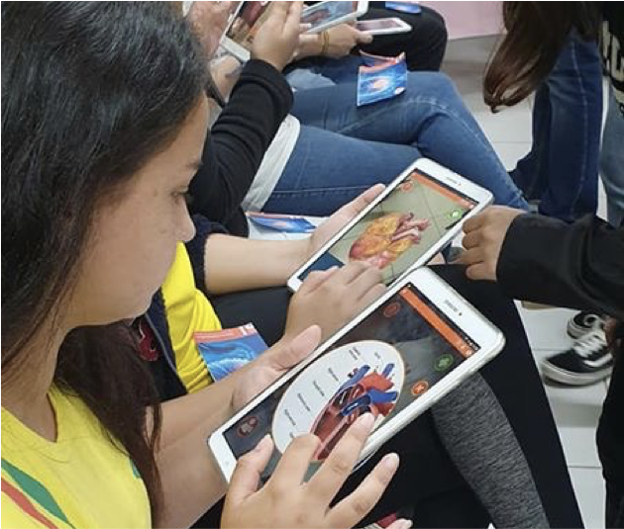

Care: Students were very engaged to investigate a real issue that they were concerned and interested in – the heart diseases and their causes. The activities were developed with professionals in Medicine and academic students in Biology and Computer Science who prepared the activities using AR resources developed by the OU.
Know: Approximately 360 Students aged from 11 to 15 used Augmented Reality to increase their knowledge about parts of the heart and its functions. They also explored a healthy and an unhealthy 3D heart.
Do: After interacting with professionals, students’ science action was to provide (do) a workshop for their parents to show the effects of smoking, drugs, alcohol and unhealthy food to their hearts. The key benefits for students were engagement, visual understanding and communication skills.
Findings: This initiative was based on a semi-structured scenario linked to the school national curriculum. This practice was organised by “RA in schools” led by UFSC University who engaged undergraduates in Medicine to work together with undergraduates in Computer science to plan activities with the open educational resources AR developed by the OU and BBC. Teachers found the activities very supportive, attractive and linked with the school curriculum. Parents found that kids were very excited and AR created more opportunity for them to show and discuss the content with them. Undergraduate students enjoyed to interact with school community and realised that they could develop more AR resources in other topics and areas.
Outcomes: Secondary school students found that AR helped them to increase their understanding about the heart. They also found activities with experts in Medicine and Computer Science useful for them to know about these areas, university and professional careers. They liked a lot the activities and were willing to use this approach again to learn other topics and also in other disciplines.
How can AI with AR be used to support students with science actions ?
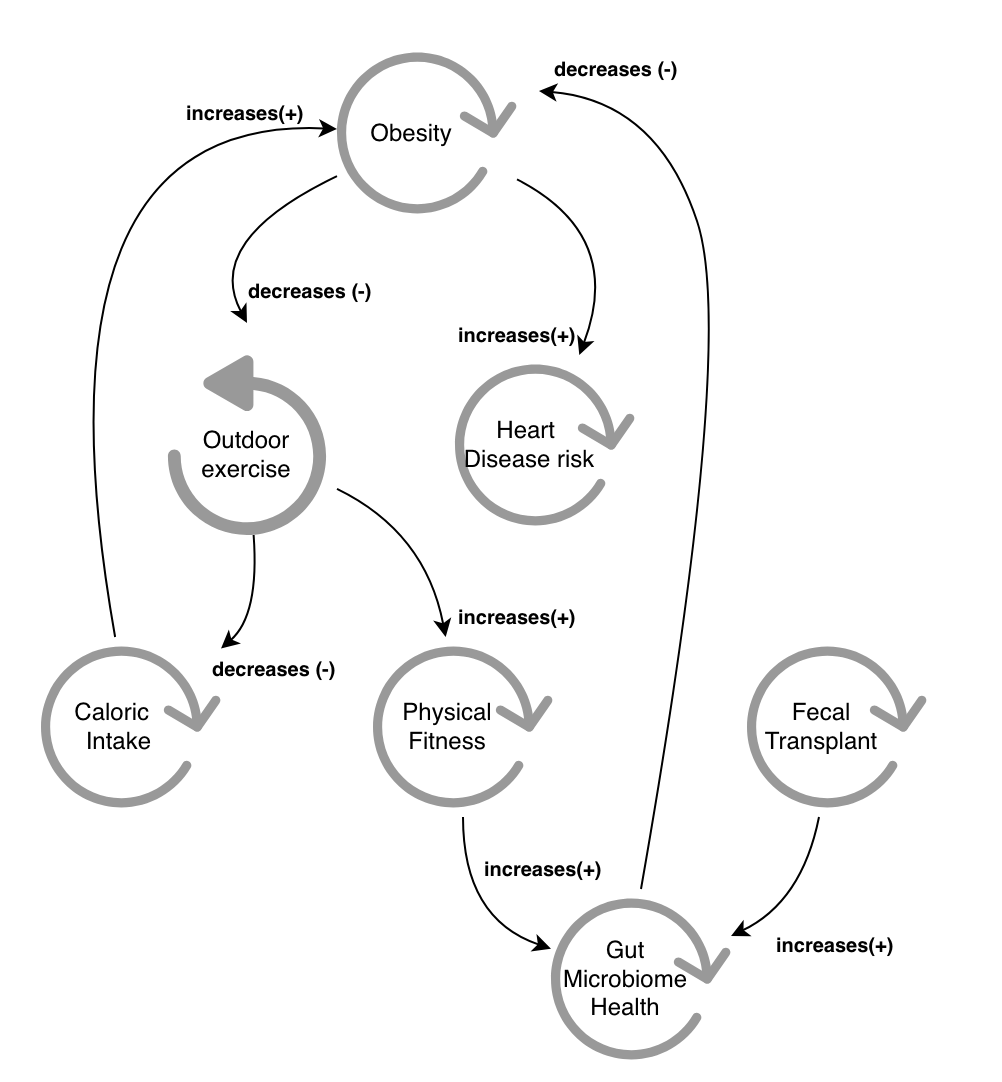
AI generated the UML code of a “casual loop map”
@startuml
!define RECTANGLE class
!define ELLIPSE actor
skinparam defaultTextAlignment center
RECTANGLE Obesity {
}
RECTANGLE “Heart Disease Risk” as HeartDiseaseRisk {
}
RECTANGLE “Caloric Intake” as CaloricIntake {
}
RECTANGLE “Outdoor Exercise” as OutdoorExercise {
}
RECTANGLE “Physical Fitness” as PhysicalFitness {
}
RECTANGLE “Gut Microbiome Health” as GutMicrobiomeHealth {
}
RECTANGLE “Fecal Transplants” as FecalTransplants {
}
Obesity –> HeartDiseaseRisk : increases (+)
HeartDiseaseRisk –> OutdoorExercise : motivates (-)
OutdoorExercise –> Obesity : decreases (-)
OutdoorExercise –> PhysicalFitness : improves (+)
CaloricIntake –> Obesity : increases (+)
OutdoorExercise –> CaloricIntake : reduces (-)
PhysicalFitness –> GutMicrobiomeHealth : enhances (+)
FecalTransplants –> GutMicrobiomeHealth : improves (+)
GutMicrobiomeHealth –> Obesity : decreases (-)
@enduml
How can AI knowledge maps with AR enhance learning about these health topics and provide a list of activities for teachers?
- Interactive 3D Knowledge Maps:
- AI generates 3D knowledge maps that students can explore in AR.
- Example: A 3D map showing connections between obesity, heart health, and gut microbiome.
- Activity: Students use AR headsets to navigate the 3D map, identifying and explaining connections between concepts.
- Personalized Learning Pathways:
- AI analyzes each student’s understanding and creates custom learning routes through the knowledge map.
- Activity: Students follow personalized AR-guided tours through the health topics, with quizzes and checkpoints along the way.
- Dynamic Causal Loop Diagrams:
- AI creates and updates causal loop diagrams as students learn, similar to the image provided.
- Activity: Students manipulate variables in the AR environment to see how changes affect the entire system (e.g., how increasing exercise impacts obesity and heart health).
- Virtual Body Exploration:
- AI generates detailed, interactive 3D models of body systems.
- Activity: Students use AR to “dissect” virtual hearts, exploring the effects of obesity on heart structure and function.
- Gut Microbiome Visualization:
- AI simulates the gut microbiome in AR, showing how it changes with diet and after fecal transplant.
- Activity: Students experiment with different dietary inputs and observe changes in the virtual gut microbiome.
- AI-Powered Health Data Analysis:
- Students input anonymized health data, which AI processes to create visual trends and predictions.
- Activity: Students use AR to explore data visualizations, identifying patterns and making hypotheses about public health trends.
- Collaborative Research Spaces:
- AI facilitates group knowledge building in shared AR spaces.
- Activity: Students work in teams to create comprehensive knowledge maps on assigned health topics, with AI suggesting connections and fact-checking in real-time.
- Virtual Health Experiments:
- AI simulates long-term health outcomes based on lifestyle choices.
- Activity: Students design virtual long-term studies on obesity prevention, using AR to fast-forward through years of simulated results.
- Argument Mapping for Health Debates:
- AI helps students construct and visualize argument maps on controversial health topics.
- Activity: Students debate the ethics and efficacy of fecal transplants, using AR to build and present their argument maps.
- Design Thinking for Health Solutions:
- AI guides students through the design thinking process to address health challenges.
- Activity: Students use AR to prototype and test obesity prevention programs, with AI providing feedback and suggestions.
- AI-Generated Quiz Landscapes:
- AI creates immersive AR environments where quiz questions are integrated into the landscape.
- Activity: Students navigate through a virtual city, answering questions about heart health and obesity as they interact with AR elements.
- Personalized Health Risk Assessment:
- AI analyzes input data to create personalized health risk visualizations.
- Activity: Students input anonymized health data and explore their personalized risk factors in AR, identifying areas for improvement.
Curriculum Links:
- Biology: Human body systems (circulatory, digestive), nutrition, metabolism, microbiology
- IT: AI and machine learning basics, data analysis and visualization, AR technology
These activities combine immersive AR experiences with AI-powered personalization to create engaging, interactive learning opportunities. They encourage students to explore complex health topics in depth, fostering critical thinking and data literacy skills while covering key curriculum points in both Biology and IT.
By integrating AI knowledge mapping tools with AR, teachers can offer students a unique, hands-on approach to understanding the interconnected nature of health issues like obesity, heart disease, and gut health. This approach not only makes learning more engaging but also helps students develop a systems thinking perspective on health and wellbeing.
Leave a Reply