This week saw UK in a Changing Europe drop a report on public opinion and Brexit.
It’s notable partly because there’s less and less in-depth exploration of this question with the passage of time: even if Brexit isn’t actually ‘done’ in poli-sci terms, it increasingly is in social and party-political ones (as witnessed by the ‘Europe policy’ wasteland of the Labour conference this week).
But it’s also notable because it reminds us that even with something as momentous as Brexit – which was genuinely A Big Deal not so long ago – publics do not hold consistent views.
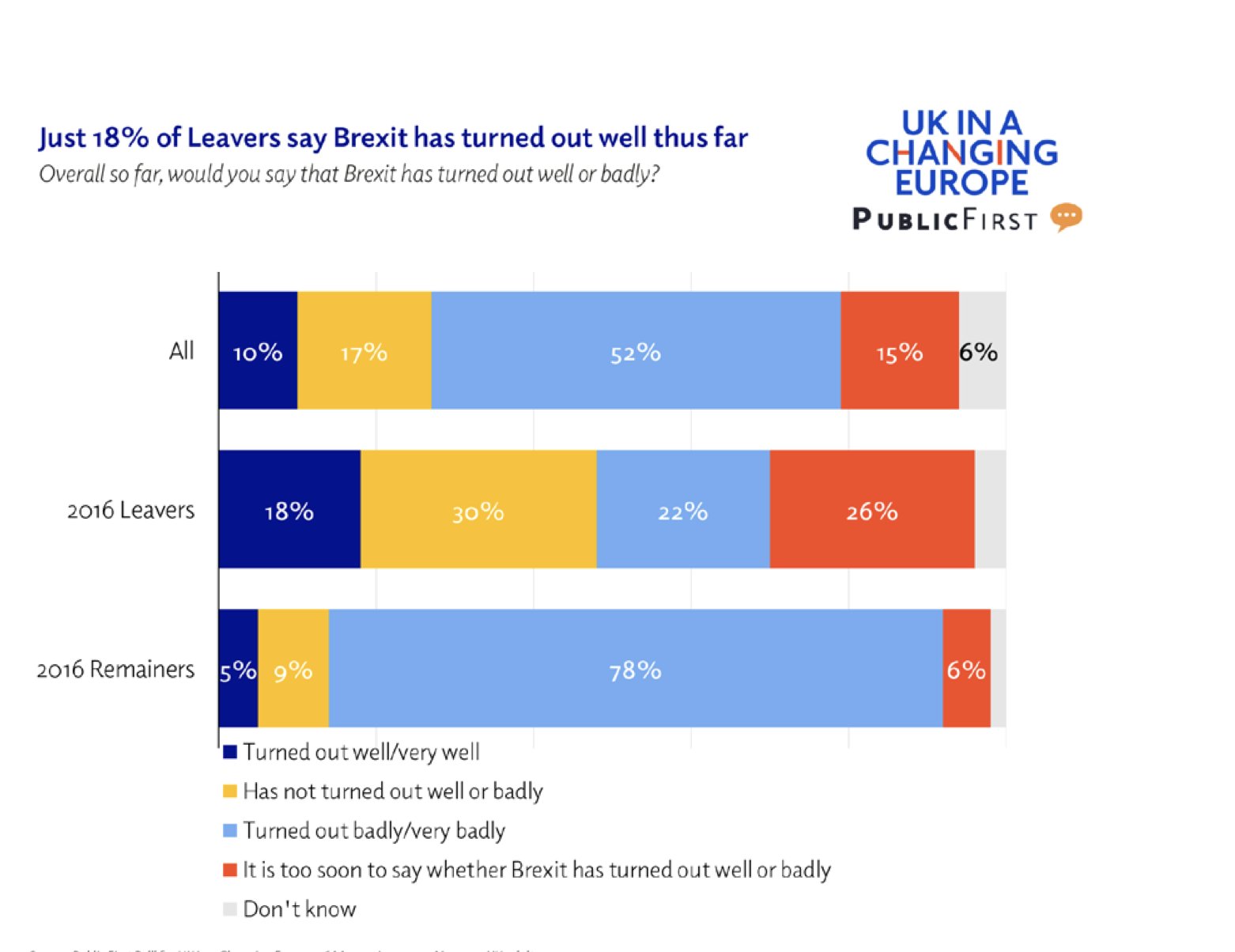
Consider this:
This is a classic chart of recent years: ‘everyone’ thinks Brexit’s a crock, regardless of voting behaviour or intention. It’s the heart of the Bregret-Rejoin narrative, wherein we realised we’ve done a terrible thing, to which the answer is to undo it all and go back to The Good Old Days.
You can look elsewhere for discussion of why this is a problematic narrative, but let’s leave it with the observation that it was precisely The Good Old Days that led to the 2016 referendum in the first place. Old? yes. Good? debatable.
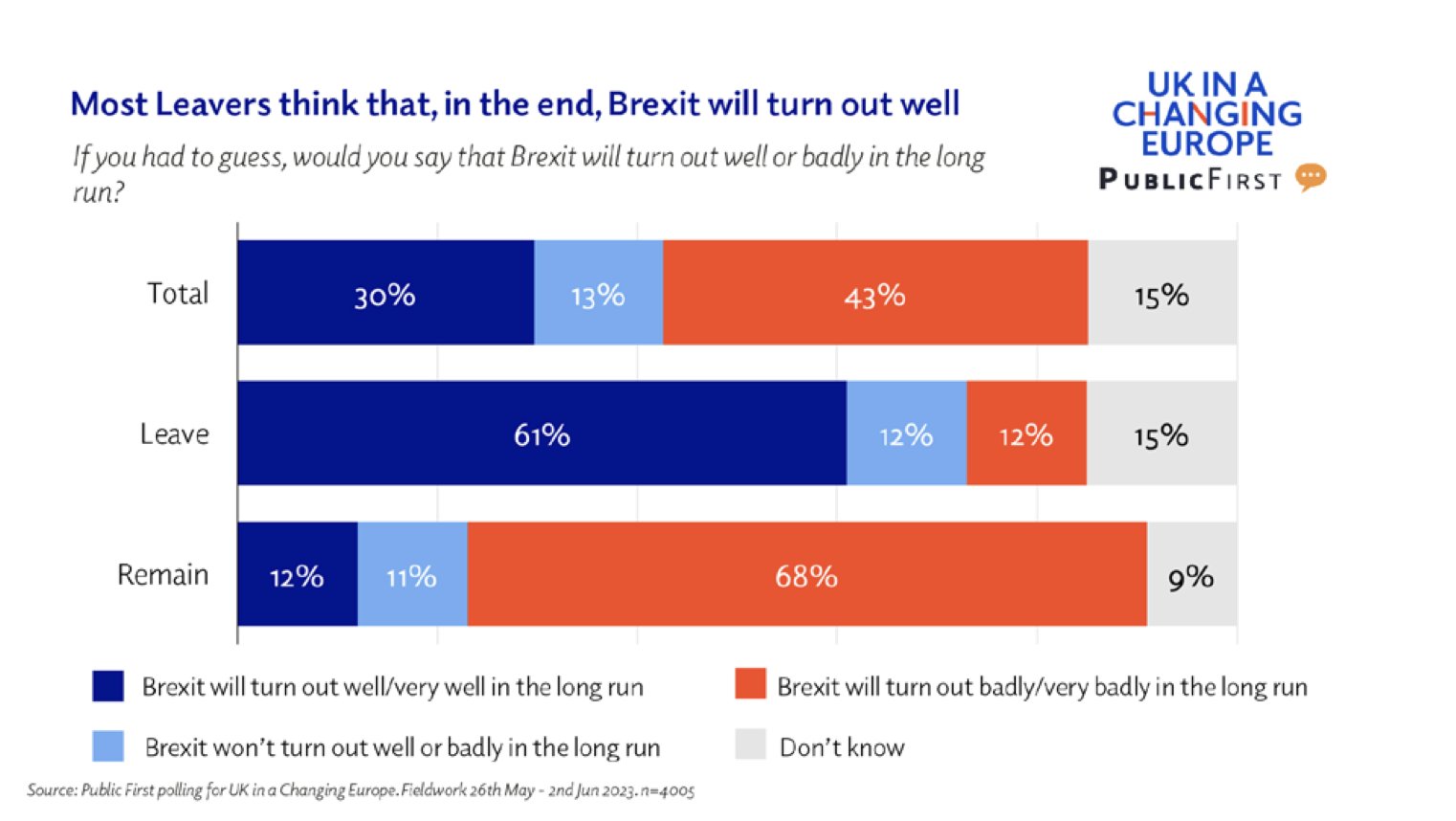
Anyway, let’s look at the next chart:
For all that most people think Brexit’s been rubbish so far, that doesn’t translate into the longer-term. A clear majority of Leavers think it can all turn the corner in the end, enough that the overall population view is much more ambivalent than the previous data might suggest.
When I tweeted about this at the time, much of the response was one of either “these people are obviously misguided” or “it’s just a minority of the population, so ignore them”.
I can understand where both views come from: the onslaught of evidence about the costs of Brexit continues week after week, while the swing from the referendum result is significant and clear.
However, it all feels like it has fallen once more into the classic traps of this domain.
The leitmotif of British European policy has always been its use to beat opponents; there has consistently been more interest in scoring domestic party political points than in finding broad consensus about the purpose of dealings with European states.
The referendum was much more a device to overturn domestic power structures than it was a considered debate on the situation of the UK in the world. Just as the fights to control the narrative of What Brexit Meant weren’t that much about EU policy but instead about owning the next generation of political discourse.
That this was both wearying and unsuccessful should be clear enough to all involved and – you might hope – would point to trying a different way of going about things. Maybe by looking for ways to reach across divides, instead of trashing those who disagree.
Maybe not.
As the referendum campaign and fallout demonstrated, rationalist arguments about costs and benefits have significant limits. People hold inconsistent views that are often more shaped (and shapeable) by emotion than cold, hard facts. ‘Take back control’ and ‘get Brexit done’ are powerful messages, whatever you think of the politics behind them (which many people didn’t think about particularly).
So yes, most people think Brexit is a mess, and yes, most people don’t think it’s ever going to turn out well. But that doesn’t mean we shouldn’t be looking for ways to build new narratives and approaches that reach out those who disagree. Otherwise, we will find that any new policy choice is neither equitable nor durable.