OU News
News from The Open University
- Home
- Category: Science
Category: Science
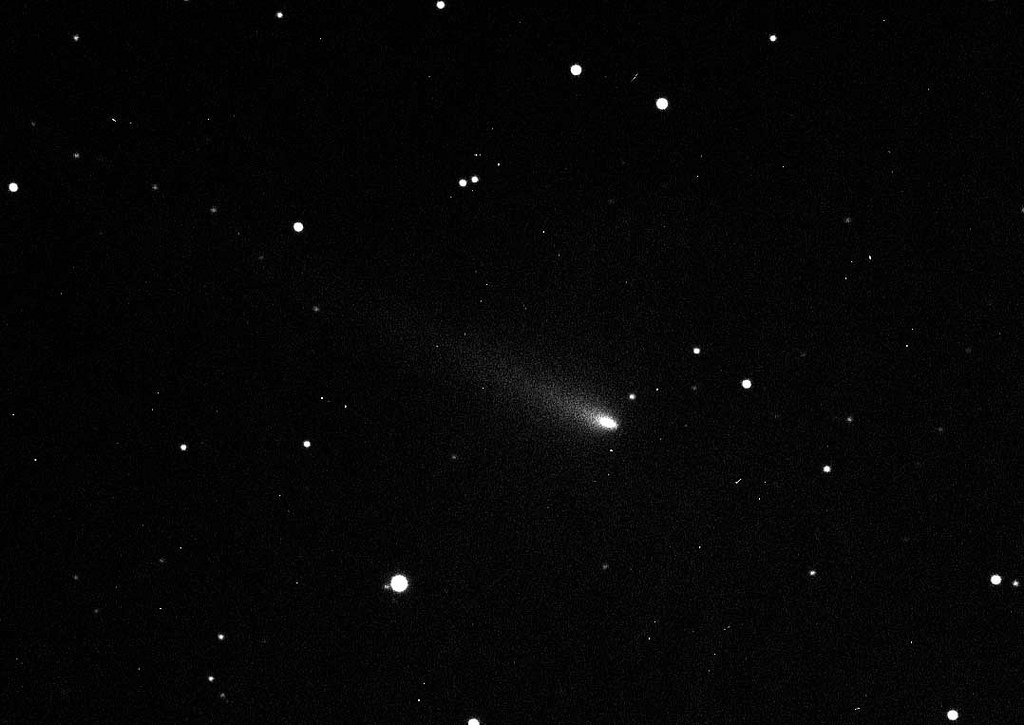

Is it a dwarf planet, an asteroid or a comet?
When Guiseppe Piazzi reported his observations of a minor planet in 1801, he originally thought it might be a comet. But follow-up observations by fellow astronomers suggested that Ceres was actually an asteroid. So it’s somewhat ironic that the latest results from NASA’s Dawn mission suggest this asteroid is confusingly similar to a comet. Dawn […]
Read more about Is it a dwarf planet, an asteroid or a comet?
Twin civilisations? How life on an exoplanet could spread to its neighbour
Imagine two nearby exoplanets orbiting the same sun, each with its own indigenous civilisation. They’re going through history either as companionable neighbours or deadly rivals. This is a familiar situation in science fiction, but could it ever happen? With the rapidly growing number of habitable exoplanets being discovered, this scenario may seem plausible. Now a […]
Read more about Twin civilisations? How life on an exoplanet could spread to its neighbour
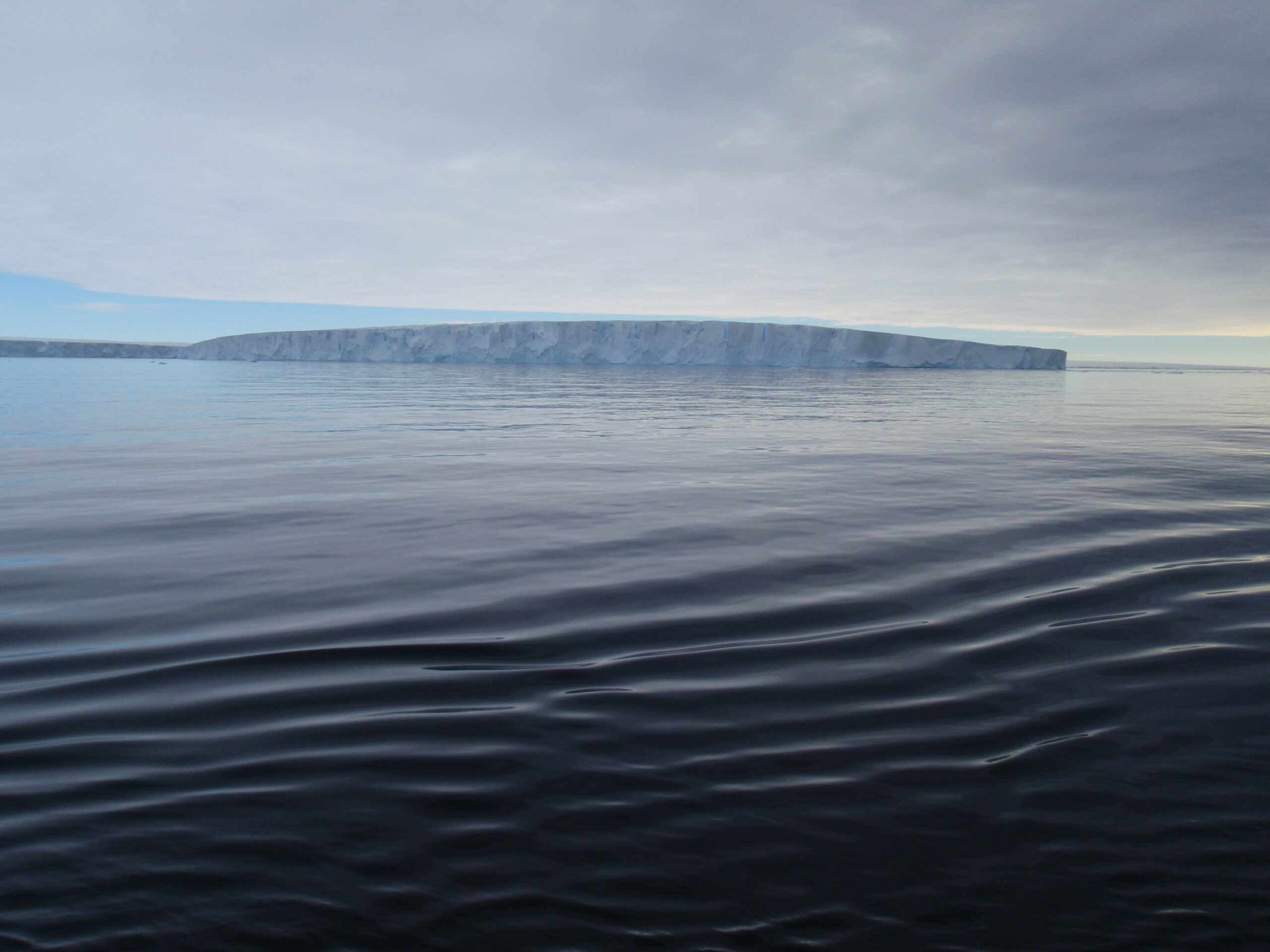

New research concludes sea-level rise may be slower than first thought
A new international study by scientists from the UK and France has concluded that, whilst melting ice in Antarctica will contribute to sea-level rise over the next century, the consequences may not be as serious as first thought. Published in the respected academic journal, Nature, the study predicts the consequences of the retreat of the […]
Read more about New research concludes sea-level rise may be slower than first thought
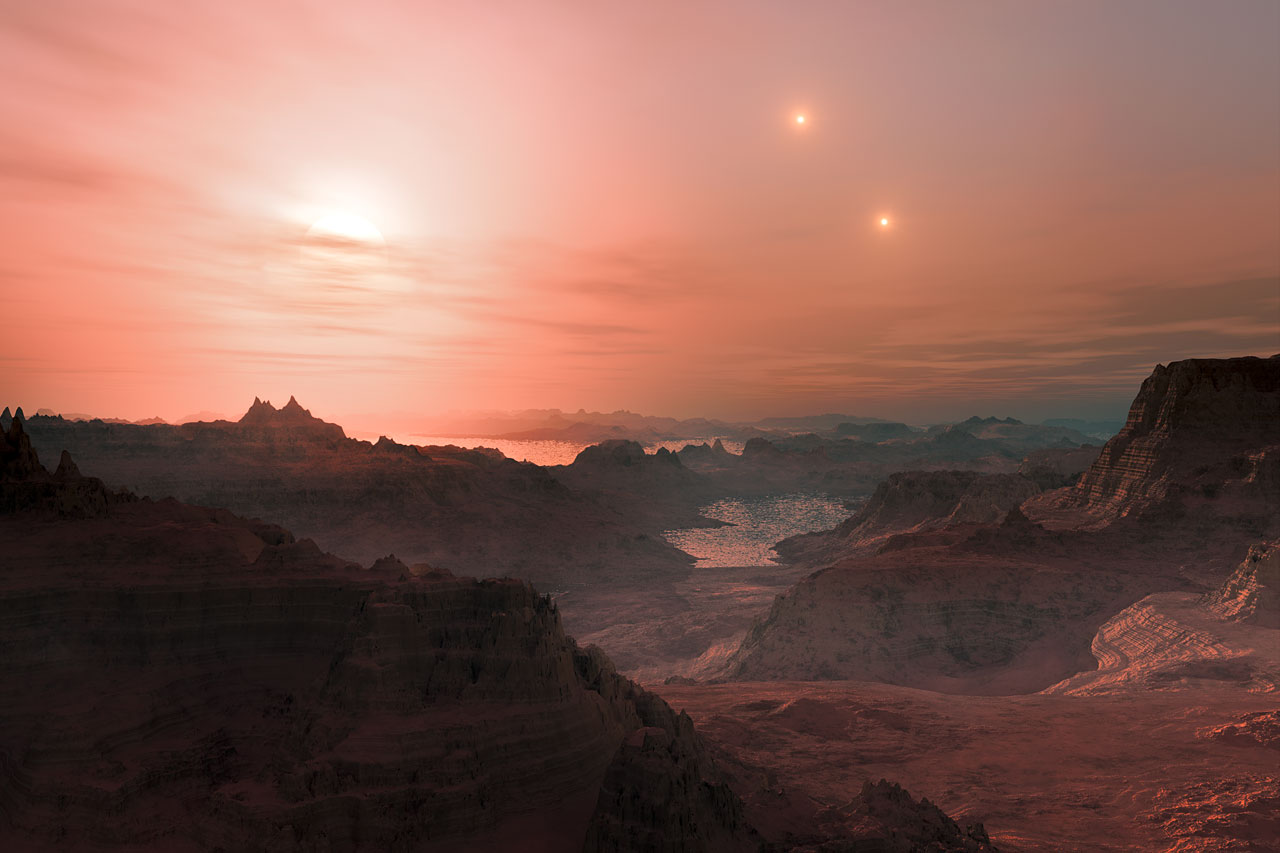

The five most Earth-like exoplanets (so far)
I’ve lost count of the number of times I’ve read that the “first Earth-like exoplanet” has been discovered. With nearly 2000 exoplanets found to date, it is no wonder so many of them will resemble our planet in some way. But which exoplanets are similar enough to the Earth that they could actually be habitable? […]
Read more about The five most Earth-like exoplanets (so far)
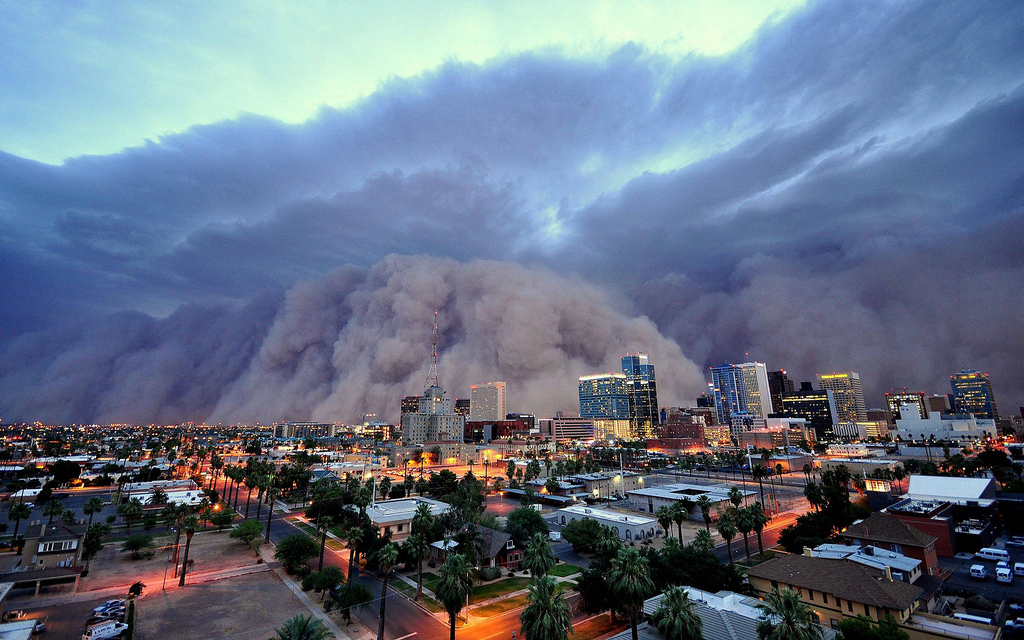

Seven spectacular weather events – and what causes them
The weather might seem like it creates weeks of dreary, grey drizzle. But it can also put on a truly sensational – and, often, deadly – show. But what explains these explosive events? The Earth’s atmosphere is driven by heating from the Sun. Weather is the response of the atmosphere to the uneven pattern of […]
Read more about Seven spectacular weather events – and what causes them
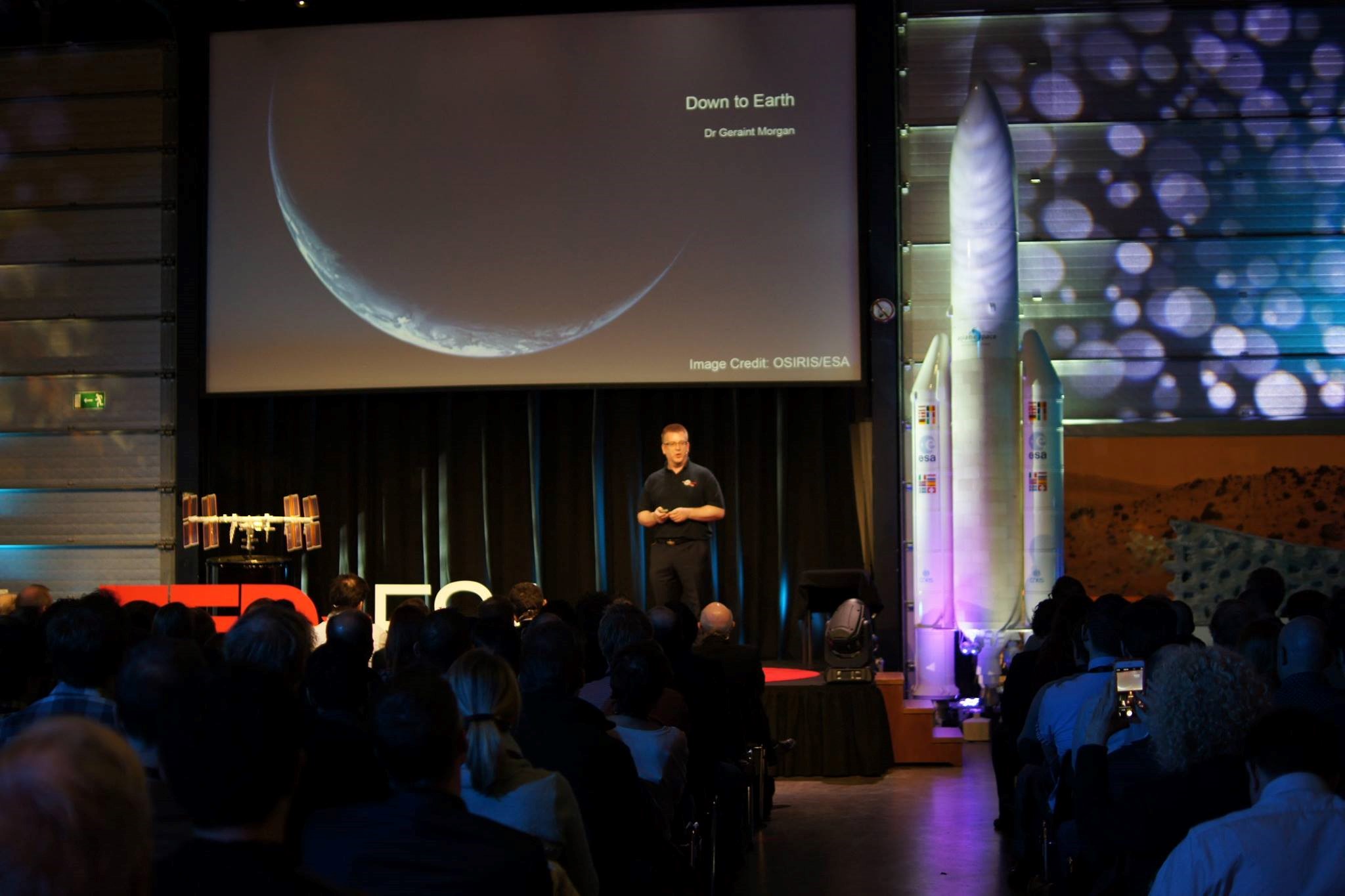

Science Beyond Fiction: OU researcher speaks at first TEDxESA Conference
OU researcher from the Faculty of Science, Geraint (Taff) Morgan, was one of 12 keynote speakers at the launch of the first ever TEDx and European Space Agency (ESA) event. In his speech, entitled Down to Earth, Taff explored how technology from the Philae lander can be translated to daily life to uncover bedbugs in […]
Read more about Science Beyond Fiction: OU researcher speaks at first TEDxESA Conference
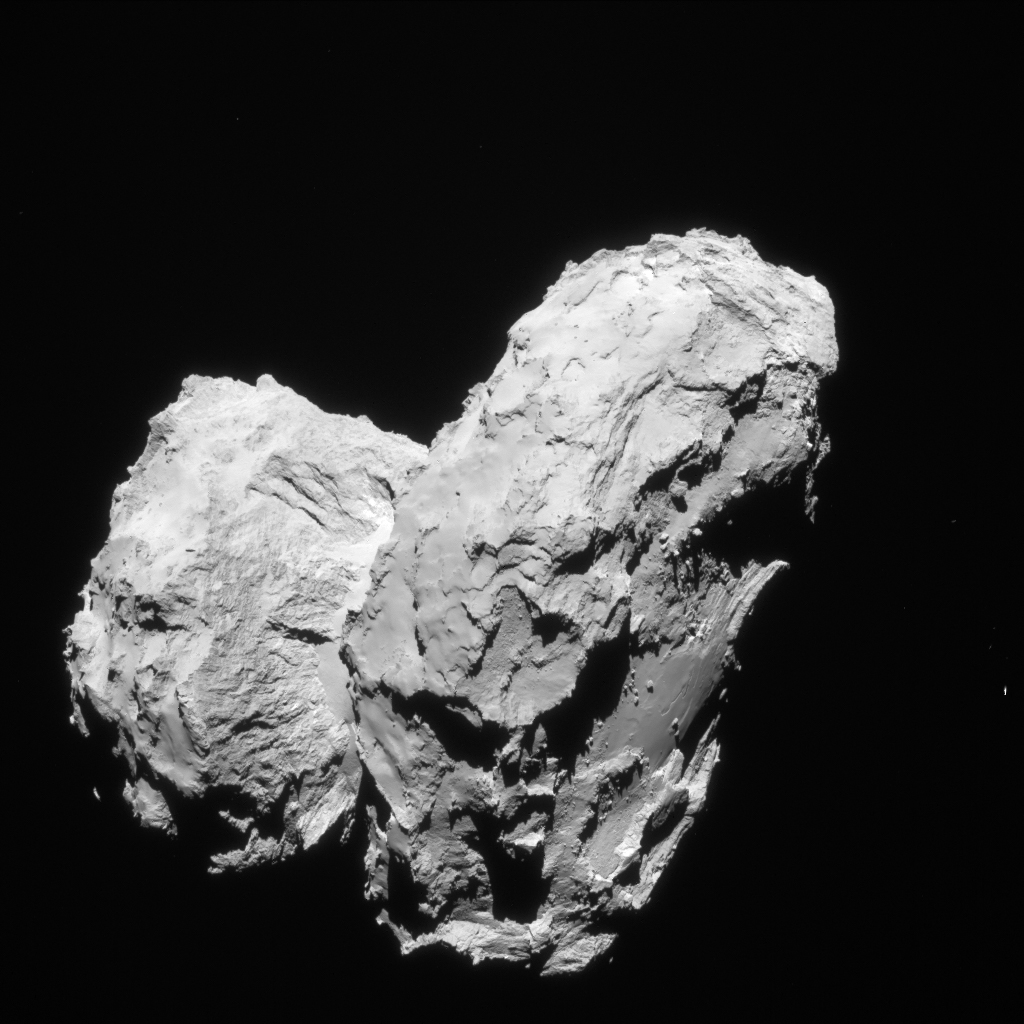

Rosetta: Surprising results from analysis of comet gases
New results from Ptolemy – the OU’s instrument on the Rosetta mission’s Philae lander – show a variance in gases coming off the comet’s surface at different locations. The new data helps researchers examine how comets are formed, and indicates that the comet was formed from different building blocks giving it a rich and diverse […]
Read more about Rosetta: Surprising results from analysis of comet gases

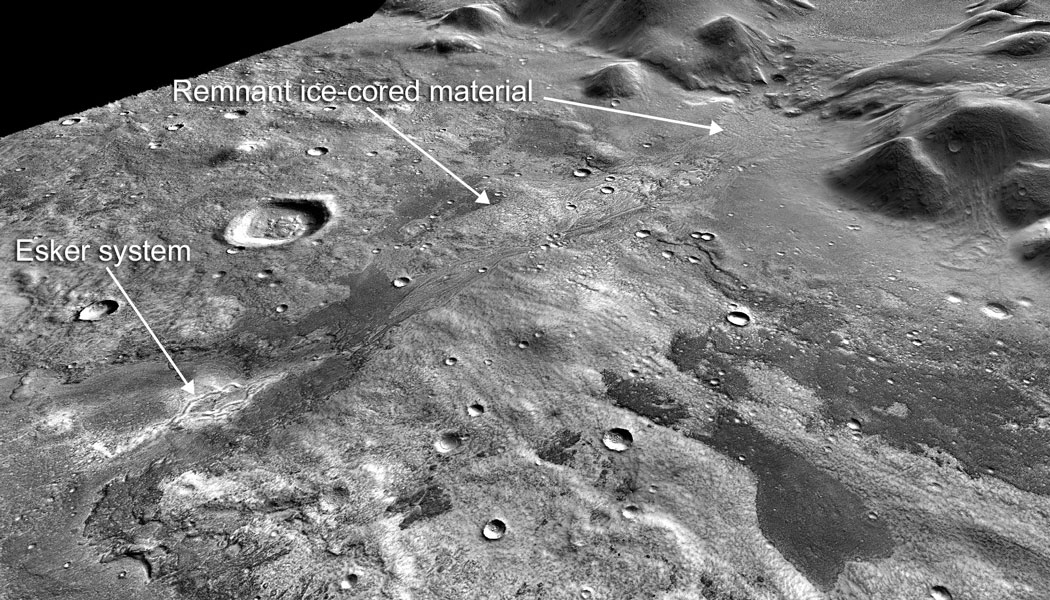
Water on Mars: evidence of glaciers similar to Earth’s
Researchers at University College Dublin (UCD) and The OU have found new evidence that liquid water flowed beneath a glacier on Mars, suggesting it had glaciers more like Earth’s than currently thought . The finding fuels the debate concerning Mars’ habitability and the burning question of whether other planets can sustain life. Dr Colman Gallagher […]
Read more about Water on Mars: evidence of glaciers similar to Earth’s

NASA: streaks of salt on Mars mean flowing water, and raise new hopes of finding life
Salty streaks have been discovered on Mars, which could be a sign that salt water seeps to the surface in the summers. Scientists have previously observed dark streaks (see image above) on the planet’s slopes which are thought to have resulted from seeps of water wetting surface dust. Evidence of salts left behind in these […]
Page 12 of 12