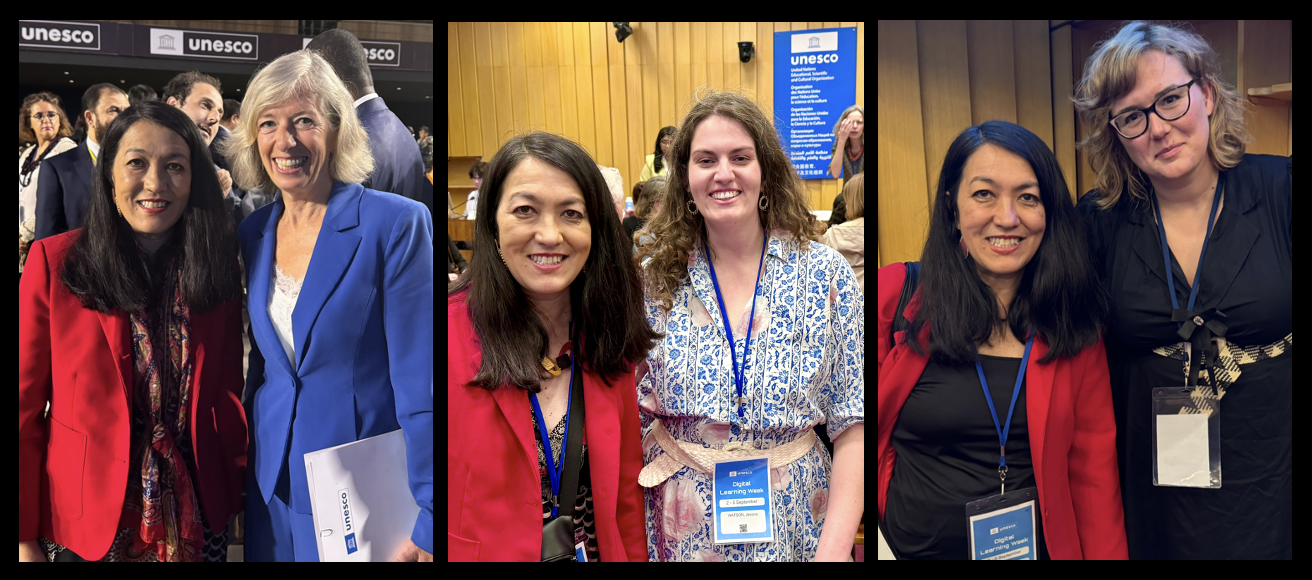
Dr. Okada from the Open University UK and representatives of CONNECT 2030 from Brazil took part in the Global Education Meeting (GEM), organized by UNESCO. This event took place in Fortaleza on October 31 and November 1, 2024, with attendance from education ministers and representatives from governments and international organizations including 194 UNESCO member countries.
The GEM provided a significant platform for discussing global education priorities, policies, and collaborations, with a focus on promoting inclusive and equitable quality education, aligning with the UNESCO’s broader mission for sustainable development.
The 2024 edition of the Global Education Meeting (GEM) has been convened by UNESCO, held every two years, GEM is one of the largest international conferences on education, bringing together ministers of education, ministers of finance, civil society, the private sector, academia, and young people from around the world. GEM 2024 aligns with the Brazilian presidency’s focus for the G20, which places equity and inclusion at its center. Thus, the meeting aims to promote multilateral, intersectoral, and multisectoral dialogue, recognizing education as a social equalizer and a driving force for sustainable development.
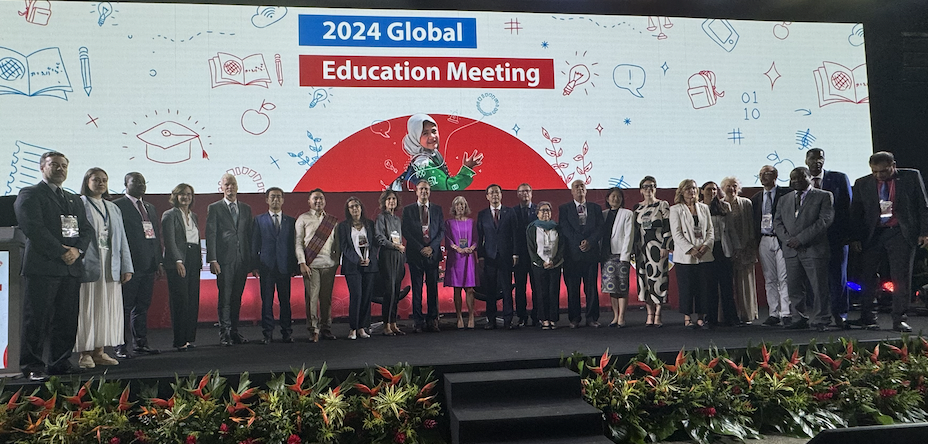

CONNECT 2030 led by Dr Okada was recognized as one of UNESCO’s top 22 global initiatives focused on digital transformation to accelerate the 2030 Agenda. This network, led by The Open University (OU) in the UK, comprises a diverse group of organizations. At GEM 2024, representatives from CONNECT 2030 included the NGO Anjos Digitais, the Secretary of Education (SEDUC) of Ceará’s government, and three universities—UFSC, UFCA, and UNEB—alongside OU-UK.
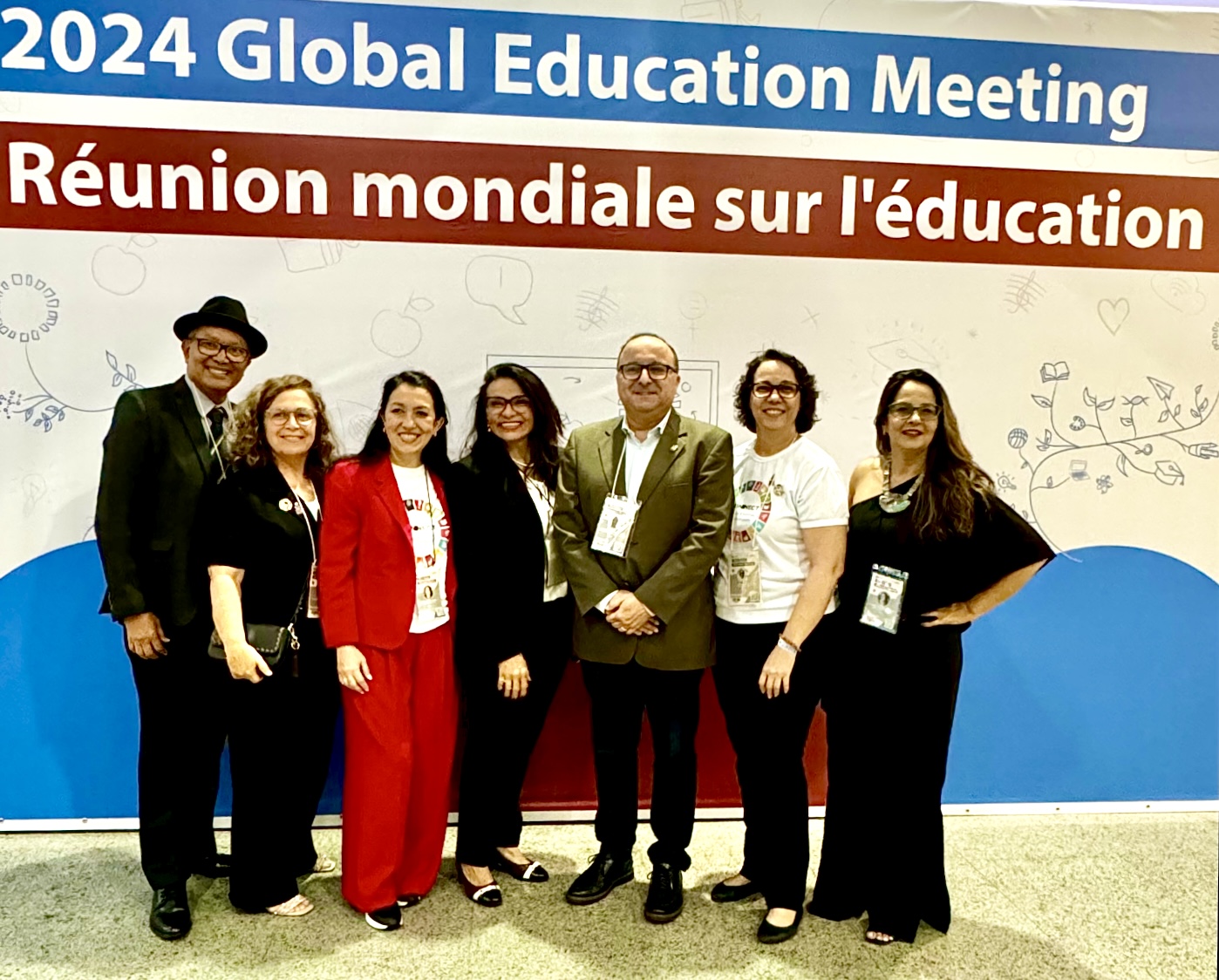

CONNECT 2030’s research practices focused on Digital Transformation to Empower Youth.

During GEM 2024, CONNECT 2030 highlighted five key initiatives focused on harnessing digital transformation to empower youth, each accompanied by specific recommendations:
- AI for Ecosystem Protection and Support for Vulnerable Communities Affected by Climate Change
Led by The OU, supported by MSC and RDE
This initiative advocates for the right of all youth, in collaboration with local communities, researchers, and AI technologies, to fully develop their potential through education centered on transversal skills and ecosystem protection. Supported by the local Secretaries of Education, the program is implemented across rainforest areas, wetlands, and fire-affected regions, including Afro-Indigenous and other vulnerable communities.
- Audiovisual Resources for Heritage and Cultural Protection and Resilience
Led by UFCA, supported by The OU
Youth are empowered to engage in creative expression through educational initiatives that preserve local culture and promote urban sustainability via digital transformation. This initiative is backed by the Secretary of Education of Ceará and involves local communities in Brazil’s semi-arid regions.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for Health and Well-being
Led by UFSC, supported by The OU
This initiative upholds the right of youth, their families, and health professionals to deepen their understanding of well-being through education enhanced by AR technologies. Supported at the national level by Brazil’s Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, it has been rolled out across the country.
- Digital Inclusion for Gender Equality and Equity
Led by Anjos Digitais, supported by The OU
Focused on empowering women with digital skills, this initiative promotes equity, diversity, and inclusion within their communities. Supported by the Brazilian government, it has been implemented in Brazil’s North and Northeast regions.
- Mobile Tools for Decent Work Against Human Trafficking
Led by UNEB, supported by The OU
This program supports youth in building awareness and advocacy against human trafficking, with educational components that offer professional support and develop transversal skills. Supported by local governments and human rights organizations, it operates in Northeast Brazil.
Global Engagement and Contributions
As a member of the UNESCO Global Education Coalition and in partnership with the Brazilian government, Dr. Okada has been invited to participate in United Nations SDG summits in the United States. She has engaged in events with global leaders at UNESCO in Europe, contributing to dialogues on Digital Education, Foundational Literacies, Artificial Intelligence, and Digital Sustainable Innovation. Dr. Okada is also actively involved in initiatives under Brazil’s leadership in the G20 and COP30.
Advancing CONNECT 2030 through GEM 2024
GEM 2024 served as a vital forum for knowledge exchange and progression of CONNECT 2030, an initiative funded by The Open University’s Open Societal Challenges program. CONNECT 2030 integrates a network of European-funded projects—including weSPOT, ENGAGE, and CONNECT—structured around the CARE-KNOW-DO framework. The network’s objectives are to promote, analyze, and expand best practices, achieving positive impacts that influence public policy and foster innovation, accelerating progress towards Agenda 2030.
Dr Okada highlited “The GEM 2024 is a significant event for The Open University, which is at the forefront of open schooling worldwide. We are honored to present our initiative alongside leaders from United Nations member countries. This is a unique opportunity to engage with ministers of education, and representatives from international organisations”

GEM 2024 presented an invaluable opportunity for knowledge exchange aligned with the Fortaleza Declaration, advancing CONNECT 2030—an integral initiative of The Open University’s Open Societal Challenges program aimed at accelerating progress toward Agenda 2030.
The Fortaleza Declaration, issued during GEM 2024 in Fortaleza, Brazil, organized by UNESCO, emphasizes education as a transformative tool for creating sustainable, fair, and peaceful societies. Below is a summary aimed at making the declaration’s key points accessible for educators.
Main Goals
- Reinforcing Education as a Right and Public Good: Education is reaffirmed as a fundamental human right that governments must protect and promote for everyone. Ensuring high-quality, inclusive education aligns with Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), which aims to provide lifelong learning for all.
- Addressing the Global Education Crisis: The declaration highlights urgent global issues like climate change, economic inequality, and the learning crisis. Currently, 251 million children and youth are out of school, and nearly 60% of children in low-income countries lack early childhood education.
- Recognizing Education as an Investment: Education is not just an expense but a vital investment for long-term societal benefits, driving economic growth, reducing inequalities, and fostering social cohesion. The declaration calls for increased education funding, especially in low-income countries, which need an additional $97 billion annually to meet their education goals.
Key Actions for Transforming Education
The declaration outlines several multi-sectoral actions to make education a powerful force for positive change:
- Climate and Environmental Education: Schools should integrate sustainability and climate resilience into their curricula, helping students and communities adopt sustainable lifestyles and prepare for climate challenges.
- Peace and Human Rights: Education systems should protect schools from conflict, promote peace and tolerance, and include human rights education to support peaceful societies.
- Gender Equality: Schools must be safe, inclusive, and free from gender-based discrimination. This includes supporting equal access for girls, especially in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields.
- Health and Well-being: Education must go beyond academics, providing health services, nutritious school meals, and mental health support to enhance students’ overall well-being.
- Technology and Innovation: Investments in digital learning and STEM should improve access to education, particularly for underrepresented groups like girls. Digital tools, including AI, should be used responsibly to enhance learning and reach students in conflict or disaster-affected areas.
Critical Areas for Progress
- Inclusive and Equitable Education: Review policies and teaching practices to ensure that all learners, especially those from marginalized groups, have fair access to education.
- Early Childhood Education: Support access to quality early childhood education, with at least one free year of pre-primary education for all, as a foundation for lifelong learning.
- Lifelong Learning: Provide flexible learning options for people of all ages, aligning education with workforce needs and promoting essential skills like critical thinking, digital literacy, and environmental awareness.
- Support for Teachers: Address teacher shortages, improve salaries, and provide ongoing professional development. Teachers should be empowered and involved in decision-making processes.
- Educational Governance and Leadership: Promote evidence-based policymaking with the participation of students, teachers, and communities. Stronger data collection and analysis are needed to ensure transparency and accountability in education.
Enhancing Education Funding
The declaration calls for increased and sustainable investment in education through:
- Domestic Resource Mobilization: Governments should expand their tax bases and allocate a minimum of 4-6% of GDP to education.
- Efficient Use of Funds: Resources must be transparently managed, targeting marginalized communities.
- Global Aid: Donor countries should increase education-focused aid, prioritizing countries furthest from achieving SDG 4.
- Debt and Innovative Financing: Countries with heavy debt should consider debt-for-education swaps, while public-private partnerships and innovative financing can also help fund education initiatives.
Commitment to Action
The Fortaleza Declaration concludes by emphasizing the need for collaborative, multi-stakeholder approaches to drive education reform. UNESCO and other international organizations will lead efforts to monitor and support SDG 4, ensuring education plays its critical role in achieving global development goals.
This declaration serves as a roadmap to guide educators, policymakers, and communities worldwide in advancing equitable, inclusive, and impactful education for sustainable development.
USEFUL Links:
Plenary sessions were recorded on the GEM webpage.
Fortaleza Declaration
Brazil United for Education
Album of Bilateral Meetings
Closing Album
Broadcasting
Access the schedule for the Global Education Meeting (GEM) 2024
G20 Education debates the relationship between school and community
SDG4_indicator_list
Broadcast: MEC YouTube Channel
News about GEM:
MEC – Ministry of Education – Brazil Government
——-










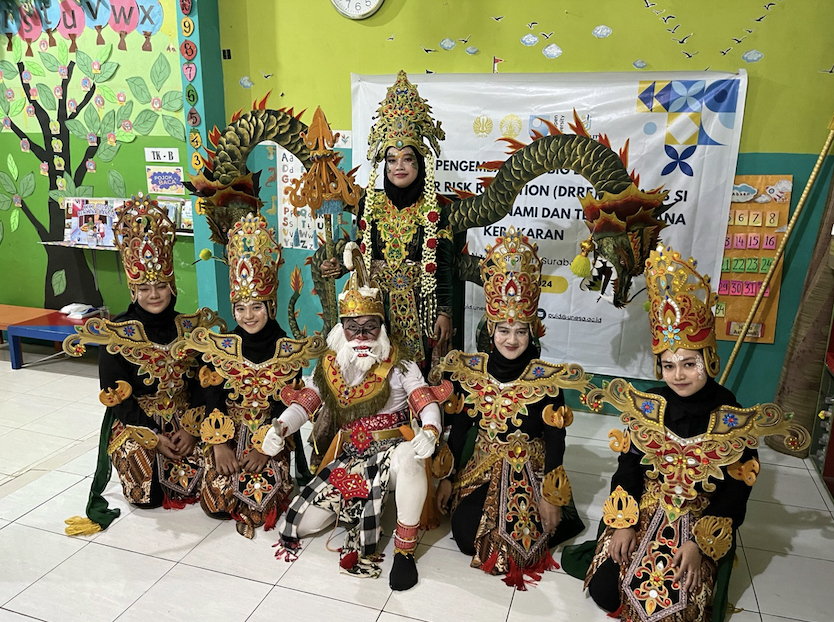
 In developing this approach further, our ongoing work has highlighted 1) the importance of creating DRRE activities that are locally and culturally relevant and 2) the need to include disabled people in the development and implementation of DRRE (Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery, 2017; Sheehy et al., 2022).
In developing this approach further, our ongoing work has highlighted 1) the importance of creating DRRE activities that are locally and culturally relevant and 2) the need to include disabled people in the development and implementation of DRRE (Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery, 2017; Sheehy et al., 2022).